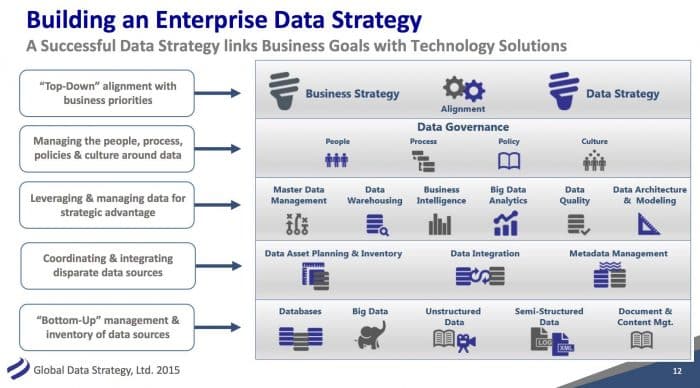
What is a Data Strategy
A data strategy is a high-level approach that outlines how an organization will collect, store, manage, and use its data. It should be aligned with the organization’s overall business goals and objectives.
A data strategy is important because it can help organizations to:
- Improve Decision-Making: By having access to data, organizations can make better decisions about their products, services, and operations.
- Increase Efficiency: By using data to automate processes and identify areas for improvement, organizations can save time and money.
- Gain Insights: By analyzing data, organizations can gain insights into their customers, markets, and operations. These insights can be used to make better decisions and improve the organization’s bottom line.
- Compete Effectively: In today’s competitive landscape, organizations that use data to their advantage have a competitive edge.
- Protect Data: By having a clear data governance policy in place, organizations can protect their data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
A well-crafted data strategy can be a valuable asset for any organization. It can help organizations to improve their bottom line, gain a competitive edge, and protect their data. Here are some specific benefits of having a data strategy:
- Increased Revenue: By using data to improve customer targeting and engagement, organizations can increase their revenue. For example, Netflix uses data to personalize recommendations for its users, which helps them to keep users engaged and subscribed to the service.
- Reduced Costs: By using data to optimize operations, organizations can reduce their costs. For example, Walmart uses data to track inventory, optimize pricing, and improve customer service. This helps them to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Improved Customer Experience: By using data to understand customer needs and preferences, organizations can improve the customer experience. For example, Amazon uses data to personalize its website and recommendations for its customers. This helps to keep customers coming back for more.
- Increased Innovation: By using data to identify new opportunities and trends, organizations can increase their innovation. For example, Google uses data to improve its search engine results and ad targeting. This helps them to attract users and advertisers.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By having access to data, organizations can make better decisions about their products, services, and operations. For example, a financial services company might use data to assess credit risk and fraud patterns in order to make better lending decisions.
If you are looking to improve your organization’s performance, then you should consider developing a data strategy. A well-crafted data strategy can help you to achieve your business goals and objectives.
Data Strategy Examples
There are many different data strategies that an organization can use to monetize data. Here are a few examples:
- Direct Data Monetization: This involves selling data to third parties. This can be done in a variety of ways, such as selling raw data, selling data insights, or selling access to a data analytics platform.
- Indirect Data Monetization: This involves using data to improve the organization’s products or services, which can lead to increased revenue or reduced costs. For example, a retailer could use data to personalize recommendations for customers, which could lead to increased sales.
- Data-driven Partnerships: This involves sharing data with other organizations in exchange for something of value, such as access to their data, expertise, or resources. For example, a healthcare provider could share data with a pharmaceutical company in exchange for funding for research.
- Data as a Service: This involves offering data as a subscription service. This can be a good option for organizations that need access to a wide variety of data but don’t have the resources to collect and manage it themselves.
The best data monetization strategy for an organization will depend on a number of factors, such as the type of data the organization has, the organization’s goals, and the target market.
Additional Considerations for creating a Data Monetization Strategy
Here are some additional considerations for creating a data monetization strategy:
- Data Governance: It is important to have a clear data governance policy in place to ensure that data is collected, stored, and used in a way that is compliant with privacy regulations and ethical standards.
- Data Security: It is also important to ensure that data is secure from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
- Data Analytics: The organization needs to have the ability to analyze data to extract insights that can be used to improve the business or monetize the data.
- Marketing and Sales: The organization needs to have a plan for marketing and selling its data to potential customers.
Data monetization is a complex process, but it can be a valuable way for organizations to generate new revenue streams and improve their business.
Data Strategy Examples
Here are some examples of data strategies in real-world organizations:
- Netflix: Netflix uses data to personalize recommendations for its users. This helps them to keep users engaged and subscribed to the service.
- Amazon: Amazon uses data to optimize its pricing, product recommendations, and logistics. This helps them to increase sales and improve customer satisfaction.
- Facebook: Facebook uses data to target advertising. This helps them to generate revenue and keep users engaged on the platform.
- Google: Google uses data to improve its search engine results, ad targeting, and other products and services. This helps them to attract users and advertisers.
- Walmart: Walmart uses data to track inventory, optimize pricing, and improve customer service. This helps them to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
These are just a few examples of how organizations are using data to improve their business. As the amount of data available continues to grow, data strategy will become increasingly important for organizations of all sizes.
Here are some other examples of data strategies in real world organizations:
- A retailer might use data to track customer spending habits and preferences in order to personalize marketing campaigns and product recommendations.
- A healthcare provider might use data to track patient health records and outcomes in order to improve patient care and make better decisions about treatment plans.
- A transportation company might use data to track traffic patterns and weather conditions in order to optimize routes and schedules.
- A financial services company might use data to assess credit risk and fraud patterns in order to make better lending decisions.
- A government agency might use data to track crime rates and traffic accidents in order to allocate resources more effectively.
These are just a few examples of how organizations are using data to improve their operations and decision-making. As the amount of data available continues to grow, data strategy will become increasingly important for organizations of all sizes.
Data Strategy for CPG Industry
The CPG industry can leverage a data strategy in several ways to stay ahead of the curve.
Here’s how data can be a game-changer.
Understanding Customer Needs and Preferences
Product Innovation
Analyze purchase history, social media sentiment, and loyalty program data to identify unmet consumer needs and product gaps. This can inform the development of new products or features that resonate with target audiences.
Personalized Marketing:
Leverage customer data to create targeted marketing campaigns and promotions. Imagine sending coupons for baby wipes to new parents or suggesting healthy snacks to calorie-conscious consumers.
Optimizing Products and Packaging
- Data-driven Design: Use data on consumer preferences and shopping habits to inform packaging design and product features. For example, analyzing shelf life data can help determine optimal packaging materials to reduce waste.
Smarter Pricing and Promotions
- Dynamic Pricing: Track competitor pricing and customer buying behavior to set optimal prices for your products. This can involve localized pricing strategies or targeted promotions based on demographics.
Supply Chain Efficiency
- Demand Forecasting: Analyze sales data and market trends to predict future demand for your products. This allows for better inventory management, reducing stockouts and overstocking, and optimizing production schedules.
- Route Optimization: Utilize data on delivery routes and traffic patterns to optimize delivery schedules, saving time and fuel costs.
Here are some additional benefits of a data strategy in CPG:
- Improved Brand Reputation: By understanding customer sentiment and addressing concerns promptly, CPG companies can build stronger brand loyalty.
- Risk Management: Data analysis can help identify potential risks in the supply chain or product safety issues, allowing for proactive measures.
Examples of Data Strategy in Action
- Company A analyzes social media data to discover a rising demand for plant-based yogurts. They leverage this insight to launch a new yogurt line catering to this trend.
- Company B uses sales data to identify a region with high demand for a specific product. They adjust production and distribution to meet this localized need.
By implementing a well-defined data strategy, CPG companies can gain valuable insights from a sea of information, ultimately making data-driven decisions that lead to increased sales, satisfied customers, and a stronger market position.